In order to understand kernel route LC-Trie,
summary the basic functions here.
NODE vs LEAF
node and leaf have two same head elements
unsigned long parentt_key key
We can treat leaf as node+leaf extention
1 | struct leaf { |
node
1 | 98 struct node { |
leaf
1 | 103 struct leaf { |
PARENT
It is a common method, hide some bit flags into the low bits of a pointer.
because the low bits always is zero(becauase of CACHE).
###the lowest 1 bit of parent is used to different node or leaf.
1 | 90 |
1 | 180 static inline struct tnode *node_parent(struct node *node) |
##BIT OPS
1 | 220 static inline t_key mask_pfx(t_key k, unsigned short l) |
tkey_extract_bits
Get value of key’s bits from the offset bit.
取 从第offset位开始的 bits位的值
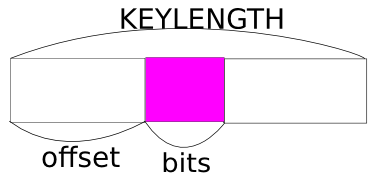
1 | 225 static inline t_key tkey_extract_bits(t_key a, int offset, int bits) |
tkey_equals
tkey a is equal with tkey b
1 | 233 static inline int tkey_equals(t_key a, t_key b) |
tkey_sub_equals
simlar with tkey_equals, while it only compare the bits bits from theoffsetst bit.
1 | 238 static inline int tkey_sub_equals(t_key a, int offset, int bits, t_key b) |
tkey_mismatch
find out the first different bit after the offsetst bit
between tkey a and tkey b.
after the operation a ^ b, the first bit with `1’ will
be the first different bit.
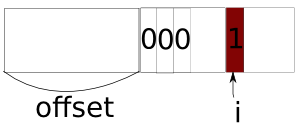
1 | 246 static inline int tkey_mismatch(t_key a, int offset, t_key b) |
mask_pfx
保留key的前l位,并将l位之后的所有位清零。l相当于掩码长度。
1 | 238 static inline t_key mask_pfx(t_key k, unsigned int l) |